Identity Verification Flow
The process of performing identity verification using Attributes on Provenance Blockchain is a crucial aspect of ensuring security and trust within the ecosystem. This process can be broken down into two main steps: obtaining a credential from an Identity Provider and presenting the credential from the user's wallet to any decentralized application (dApp).
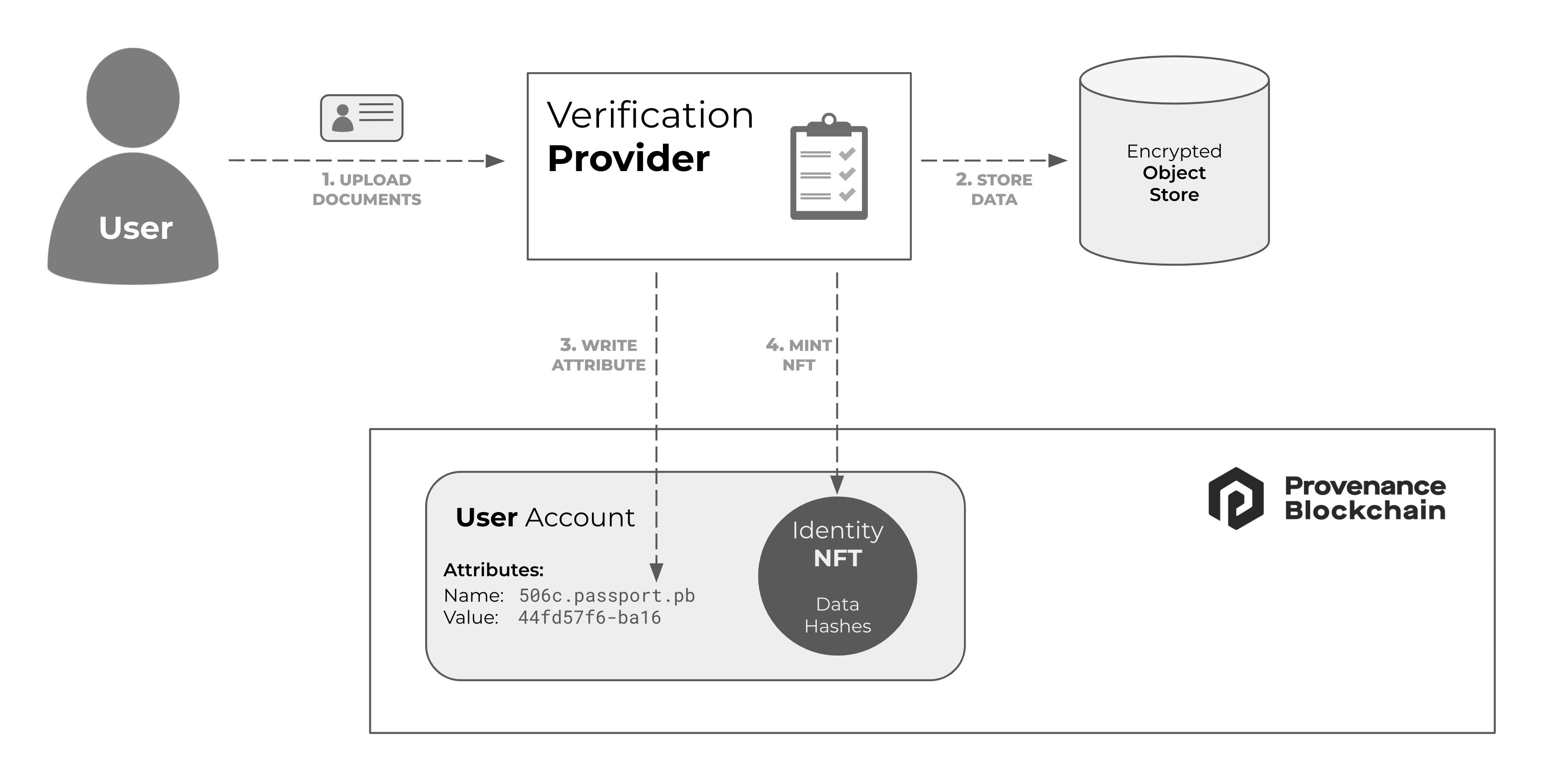
Step 1: User Undergoes KYC
The user is typically directed to an Identity Provider from an application (dApp).
- To initiate the process, the user must visit an identity verification provider company.
- The identity verification process involves the user providing personal information (name, date of birth, address) and submitting relevant documentation to confirm their identity. Documentation requirements may vary based on the level of verification needed by the application or service. or example, some services may require a government-issued ID, while others may require additional documents such as proof of address or proof of income.
- Upon completing the verification process, the provider writes an Attribute to the user's account on the Provenance Blockchain, indicating that the user has passed the verification requirements. This Attribute serves as proof of completion and can grant access to specific features or services within the Provenance ecosystem.
- The identity verification provider stores the verification data in the Encrypted Object Store (EOS), which coordinates with Provenance Blockchain NFT records. By storing the data in the EOS, the provider ensures data security and immutability.
- The provider also creates a unique NFT (non-fungible token) representing the verification data on the blockchain. This NFT allows the user to own their verification data as an asset in their account or wallet, ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive information.
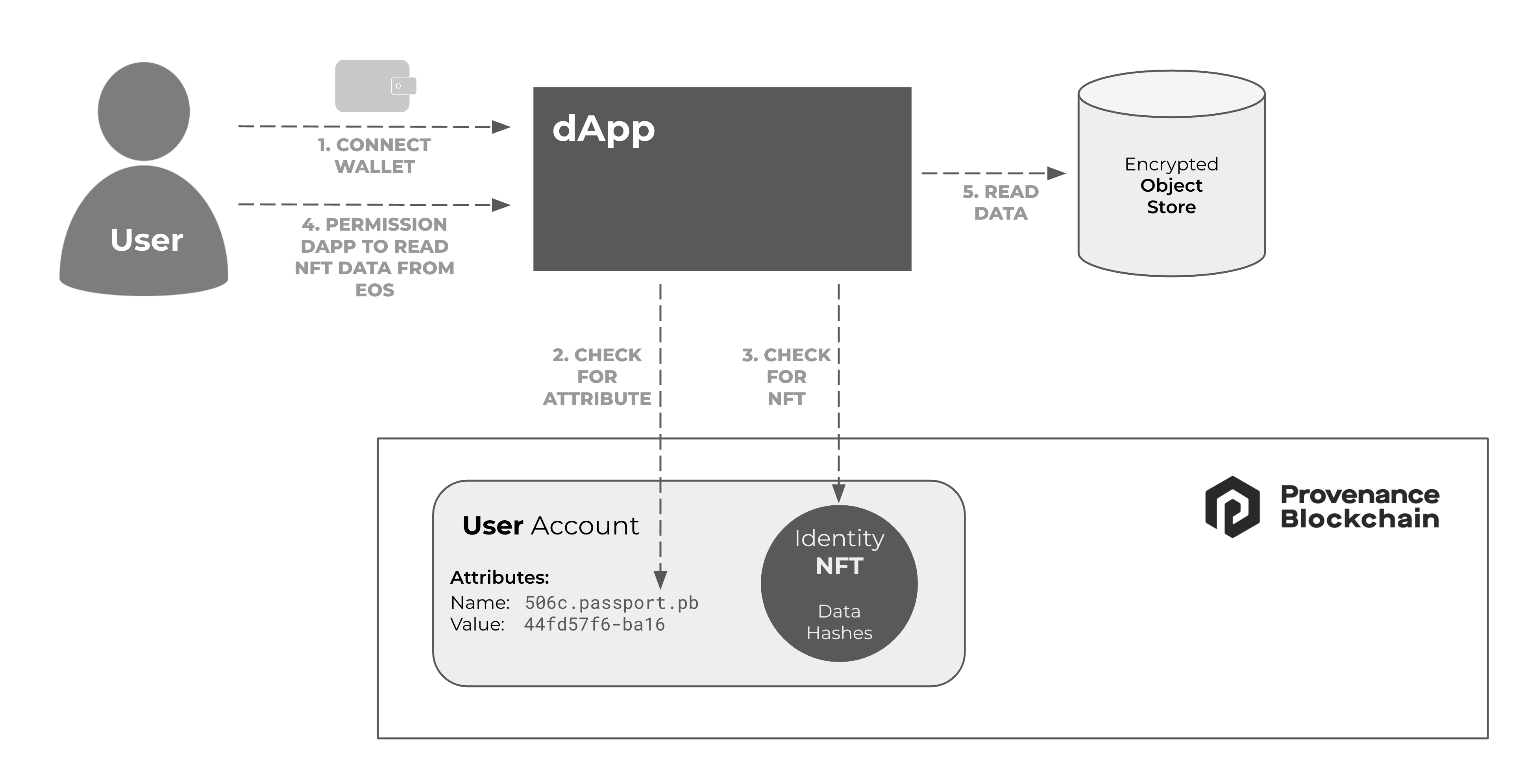
Step 2: User Grants dApp Permission to Read KYC
User KYC Attributes can be utilized in two ways:
- The dApp or smart contract can make decisions based on the Attribute's presence or absence and name. If the Attribute exists, it means the user has met the requirements for the credential. In many cases, this check is sufficient to complete the business process.
- If the credential use case requires the full identity verification data, the dApp can request permission from the user to read the data stored in the EOS.
The method for accessing NFT identity data depends on the Identity Provider. The provider could make the EOS Gateway available to application users or provide an API to fetch the data. For more information on the design and availability of Identity NFTs, refer to the Identity NFTs section.