dApp Architecture
Full-Stack dApp
A full-stack dApp (web or mobile app) using Provenance Blockchain typically consists of several layers and components that work together to provide a seamless and secure experience for users. Here is a high-level overview of the architecture:
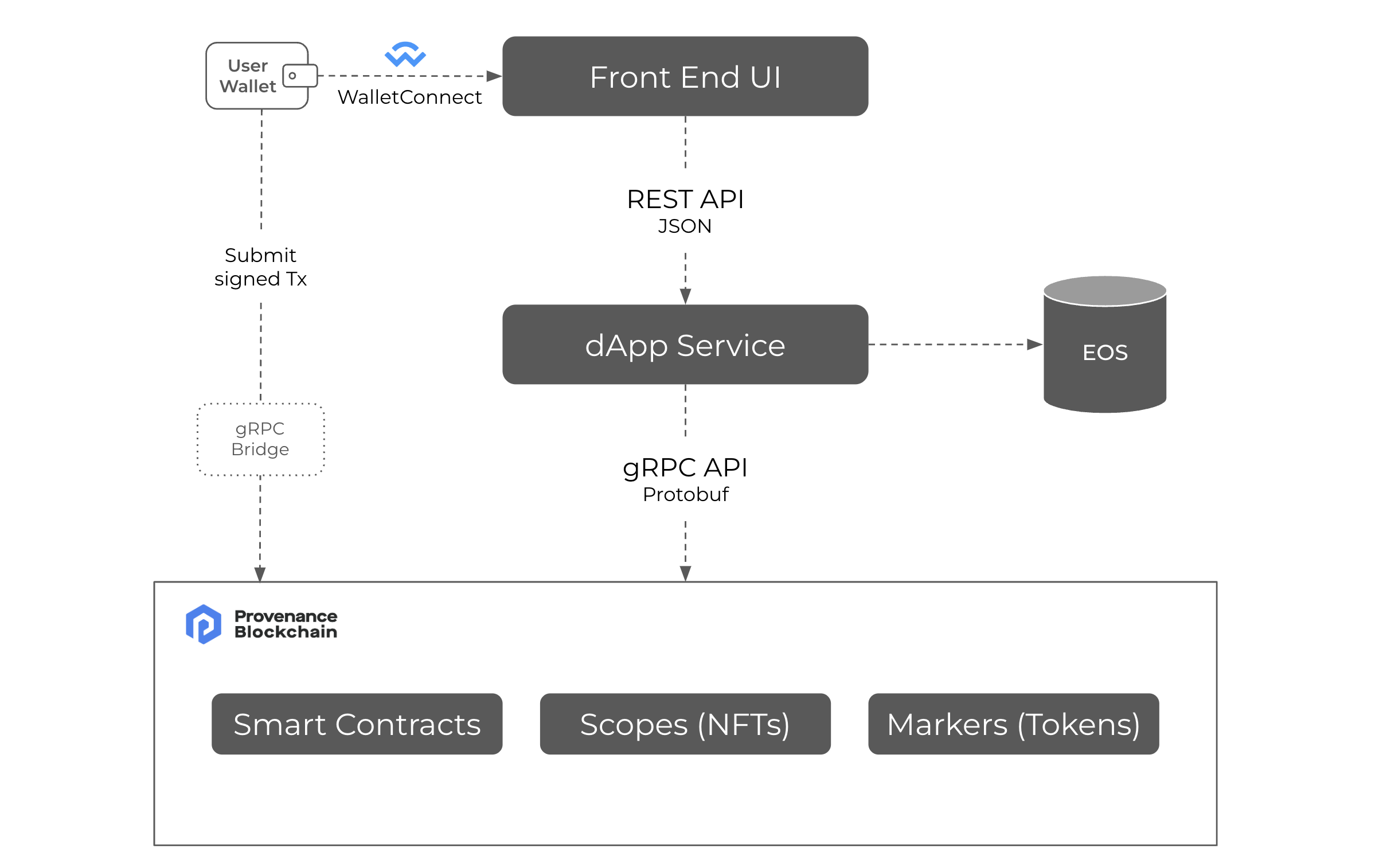
Frontend Layer: The frontend layer is responsible for rendering the user interface and handling user interactions. It is usually built using modern web or mobile app technologies like React, React Native, Vue, Angular, or Swift for creating responsive and interactive interfaces. This layer communicates with the backend layer through APIs to perform various tasks.
Backend Layer: The backend layer manages the business logic and data processing of the dApp. It often includes a server or serverless architecture, built using technologies like Node.js, Python, or Java, which exposes RESTful or GraphQL APIs for the frontend to consume. The backend layer communicates with the Provenance Blockchain to read and write data, interact with smart contracts, and perform other blockchain-related tasks.
BlockVault and EOS (Encrypted Object Store): BlockVault provides a secure and privacy-preserving storage solution for your dApp by leveraging the Encrypted Object Store (EOS). EOS is a storage system that enables the encryption of sensitive data before storing it on the Provenance Blockchain. By integrating with BlockVault and EOS, your dApp can benefit from an added layer of security, ensuring that user data remains protected and confidential while maintaining the integrity of the information stored on the blockchain.
Provenance Blockchain: The Provenance Blockchain forms the core of the dApp, providing a decentralized and secure ledger for storing and managing data. The blockchain ensures data integrity and security. Smart contracts are deployed on the Provenance Blockchain to define and enforce the rules of the dApp, such as token issuance, trading, and compliance.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are programs that run on the Provenance Blockchain. They are written in Rust and are used to automate processes, enforce rules, and manage data in a transparent and decentralized manner. Smart contracts can be used to define the logic for token issuance, transfer restrictions, investor accreditation, and other regulatory requirements.
Wallet: The wallet is an important component in the architecture, enabling users to securely manage their digital assets and interact with the dApp. Wallet: As a dApp builder, you don't need to create a new wallet for your application. Instead, you can leverage any of the available ecosystem wallets that support WalletConnect. This allows users to securely connect their wallets to your dApp, enabling seamless transactions and interactions with the Provenance Blockchain. By integrating with existing wallets, you can focus on building your dApp's core functionalities and enhance the user experience.
External Services: dApps may also integrate with external services to enhance their functionality, such as identity verification providers for KYC/AML checks, oracles for real-time data feeds, and payment gateways for fiat currency transactions.
In summary, a full-stack dApp using the Provenance Blockchain combines a frontend layer, backend layer, smart contracts, and a wallet to provide a secure, transparent, and efficient experience for users. The architecture is designed to facilitate seamless interaction between the various components, leveraging the power of the Provenance Blockchain and external services to deliver a comprehensive and innovative solution.