Identity Verification on Provenance Blockchain
Identity verification processes, such as Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), and 506(c) investor accreditation, are critical for ensuring the security and integrity of financial and blockchain systems. However, managing these processes can be a complex and challenging task, requiring significant time and resources.
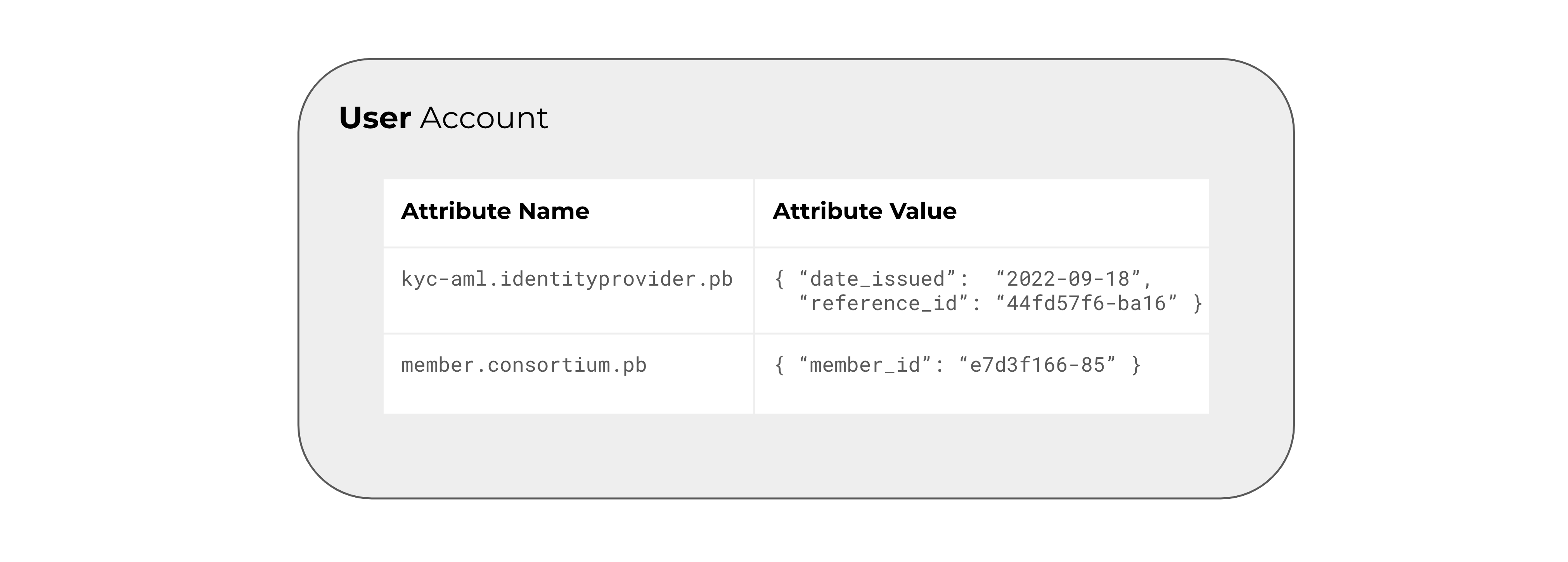
To simplify and streamline the identity verification process, Provenance Blockchain has developed a solution that uses Attributes, a name-value pair structure that allows for the storage and management of verified identity information on the blockchain. Attributes are essentially metadata added to a blockchain account to indicate that an individual or entity has passed a specific verification process.
For instance, an attribute might be used to verify that a person has completed a KYC process or that an entity is accredited to invest in a particular security. The data stored in the attribute value can be of various types, including text, JSON, URL, UUID and other formats.
One of the main benefits of using attributes on Provenance Blockchain is that it allows for automatic verification of identity. Smart contracts can verify that a participant has met specific criteria by checking the attribute values stored on the blockchain. This approach can significantly reduce the need for manual identity verification and improve the accuracy of the process.
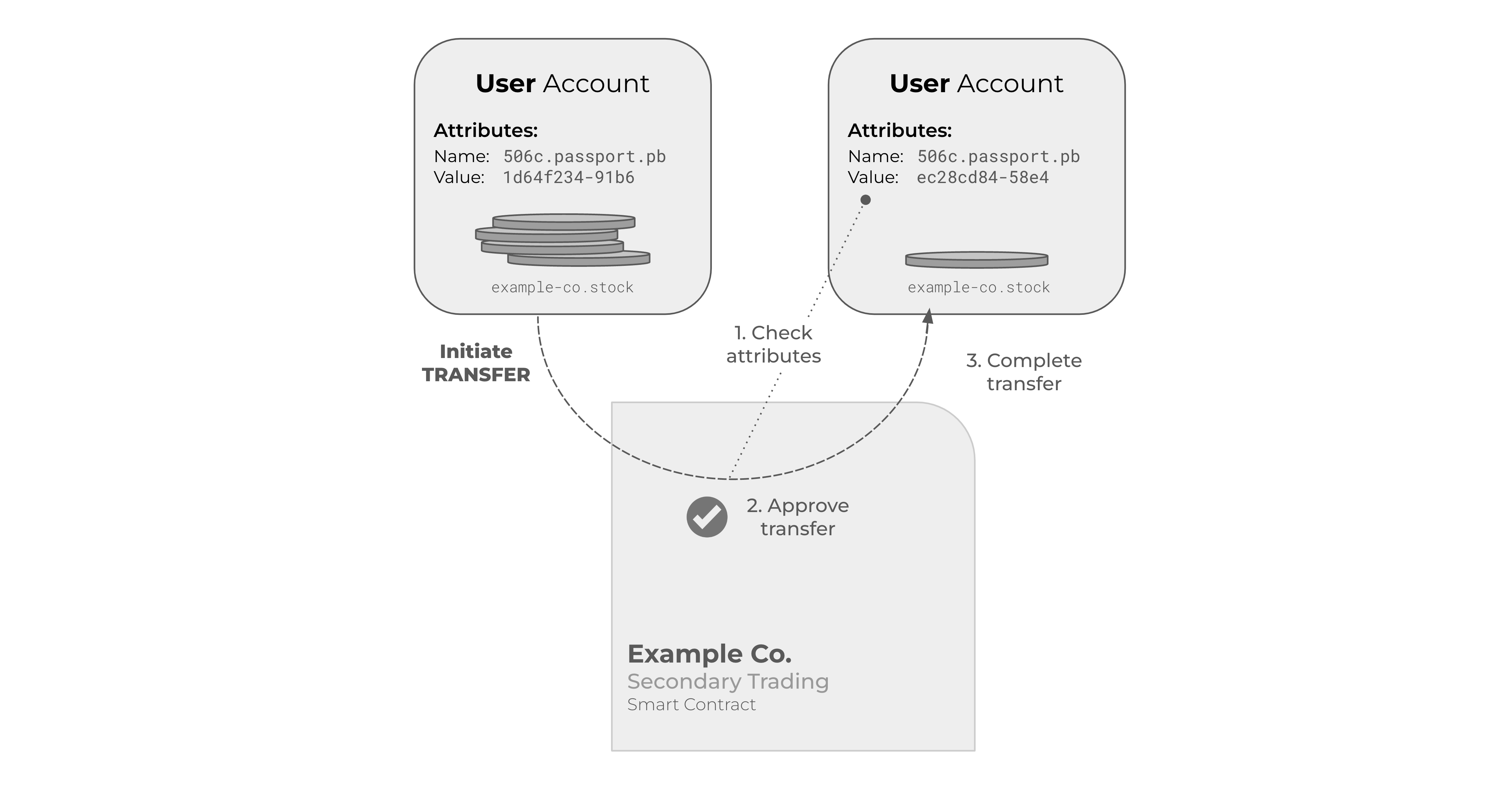
Attributes provide a standardized way to manage identity verification records across different financial applications. Different smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) can choose which identity verification providers they accept, either by using a wildcard expression or by requiring a specific attribute from a particular provider. This flexibility allows for a wide range of use cases, from simple one-time identity verification to more complex ongoing verification processes.
Rich Verification Data
On Provenance Blockchain, smart contracts can read and analyze the data stored in the attribute value for an account. However, some applications may require a more comprehensive set of data, which can be shared by the verification provider.
One option for sharing this data securely with dApps is for the verification provider to store the data in a secured relational database and make it available to dApps through REST API calls. However, this approach requires negotiation between each dApp and each verification provider (for example, establishing an API key for access), which can be time-consuming and cumbersome.
A better way to share user verification data is to create an NFT (Scope) that represents the user's
credentials and is stored in their account on the blockchain. This way, the digital identity credential can be stored as
an NFT in the user's wallet and can be easily shared with other dApps.
The verification data is stored in Provenance's Encrypted Object Store (EOS), which provides a secure and private location for the data to be stored. The user can then permission their own EOS credential data to the dApp of their choosing, allowing them to share their identity information without compromising their privacy or security.