Provenance Blockchain (BlockVault) Contract Execution Environment
BlockVault was designed to directly integrate with the Provenance Blockchain Metadata Module to simplify generating signed records of an asset’s Provenance Blockchain as either a single party or in conjunction with multiple interacting parties. At its core, BlockVault is a GRPC API that is invoked using a Kotlin SDK. The API processes data through a deterministic client side process that can be shared with other parties to transform data into a hashable format.
Assets can be directly defined against the Metadata module, but the execution environment assists in the complex hashing of data, maintenance of immutable objects, and signature orchestration between multiple parties.
Client Contracts
Client side contracts differ from Smart Contracts in that they keep your data private between parties off chain and allow a structure to record agreed upon state data to the blockchain. Smart contracts in comparison are running on the blockchain and require the validators to have access to the data which isn’t a great solution for most consumer based transactions due to data privacy laws.
Transaction Flow
The following diagram outlines the flow of data for typical transactions proposed to Provenance Blockchain.
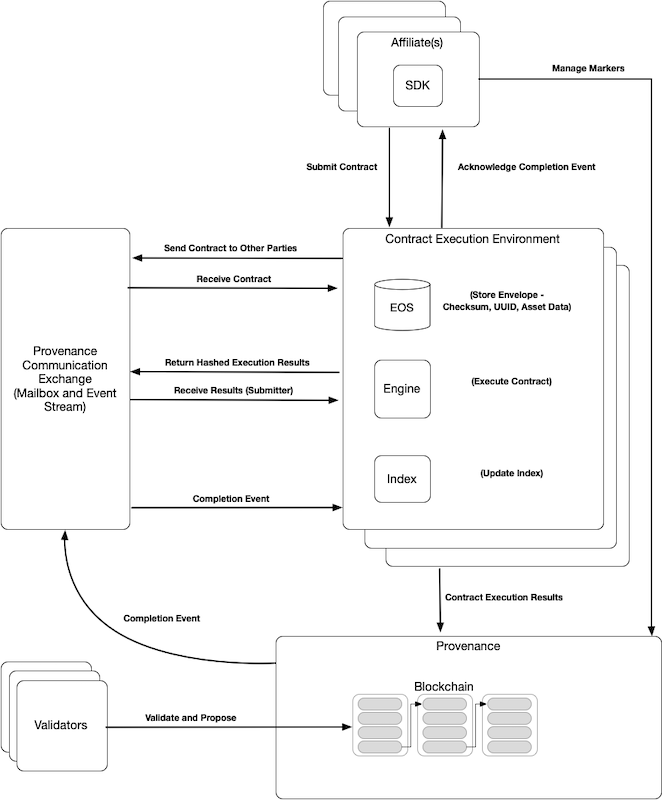
- Affiliates utilize the Contract Execution Environment to submit contracts to create single or multi-party agreements.
- The contracts and asset data are forwarded to all affiliates participating in the contract.
- Each affiliate’s Encrypted Object Store is updated with the encrypted asset data resulting in each participating affiliate having a copy of the asset data.
- Using their copy of the asset data, each affiliate participating in the transaction executes the contracts.
- The hashed results of the contract executions are returned to the submitting affiliate’s execution environment.
- All hashed execution results are sent to Provenance Blockchain.
- The hashed results are validated by the validators. If the majority agree, the transaction is proposed to the blockchain.
- Provenance Blockchain emits events notifying affiliates the contract has been committed on the blockchain.
- The index is updated with the new contract information. This information is used later for searching and querying the data.
- Affiliates acknowledge the completion event.
For certain transactions, affiliates can also interact directly with Provenance Blockchain without utilizing or even needing a Contract Execution Environment. For example, markers are managed by directly interacting with Provenance Blockchain instead of executing contracts.